uml小组作业(第二次)
题目
设计一个图书馆管理系统的UML类图和对象图,并将类图转换成Java代码。该系统需要管理用户、书籍、借阅记录、罚款和通知等功能。
类图
请根据要求,设计出相应的UML类图,确保所有的类和关系都被正确地表示和连接。 类定义要求:
- 在这个系统中,用户(User)是一个基础实体,拥有唯一标识符(id)、姓名(name)和用户类型(type). 用户可以执行登录(login)和登出(logout)操作。
- 书(Book)实体包含唯一标识符(id)、书名(title)和作者(author),还有一个布尔值(isBorrowed)来表示书籍是否已被借出。 书籍可以被借出(borrow)和归还(returnBook)。
- 读者(Reader)是用户的一个子类,除了继承用户的基本属性外,还包含一个已借书籍列表(borrowedBooks)。 读者可以借书(borrowBook)和还书(returnBook)。
- 管理员(Admin)也是用户的一个子类,具有添加书籍(addBook)、移除书籍(removeBook)和管理用户(manageUsers)的权限。 借阅记录(LoanRecord)记录了借阅的详细信息 包括借阅记录ID(LoanRecordId)、借阅者的ID(readerId)、书籍ID(bookId)、借阅日期(borrowDate)、到期日期(dueDate)和实际还书日期(returnDate)。 它可以创建新的借阅记录(createLoanRecord)和更新还书日期(updateReturnDate)。
- 罚款(Fine)实体涉及借阅记录ID(loanRecordId)和罚款金额(amount),可以计算罚款(calculateFine)和支付罚款(payFine)。
- 通知(Notification)实体用于发送通知给用户,包含接收通知的用户ID(userId)、消息内容(message)和发送日期(sentDate) 可以发送通知(sendNotification)。
关系要求: 用户(User)是读者(Reader)和管理员(Admin)的父类。 读者(Reader)和书籍(Book)之间存在多对多的关系,通过借阅记录(LoanRecord)实现。 借阅记录(LoanRecord)与读者(Reader)和书籍(Book)都是一对一的关系。 罚款(Fine)与借阅记录(LoanRecord)是一对一的关系。 通知(Notification)可以向任何用户(User)发送。
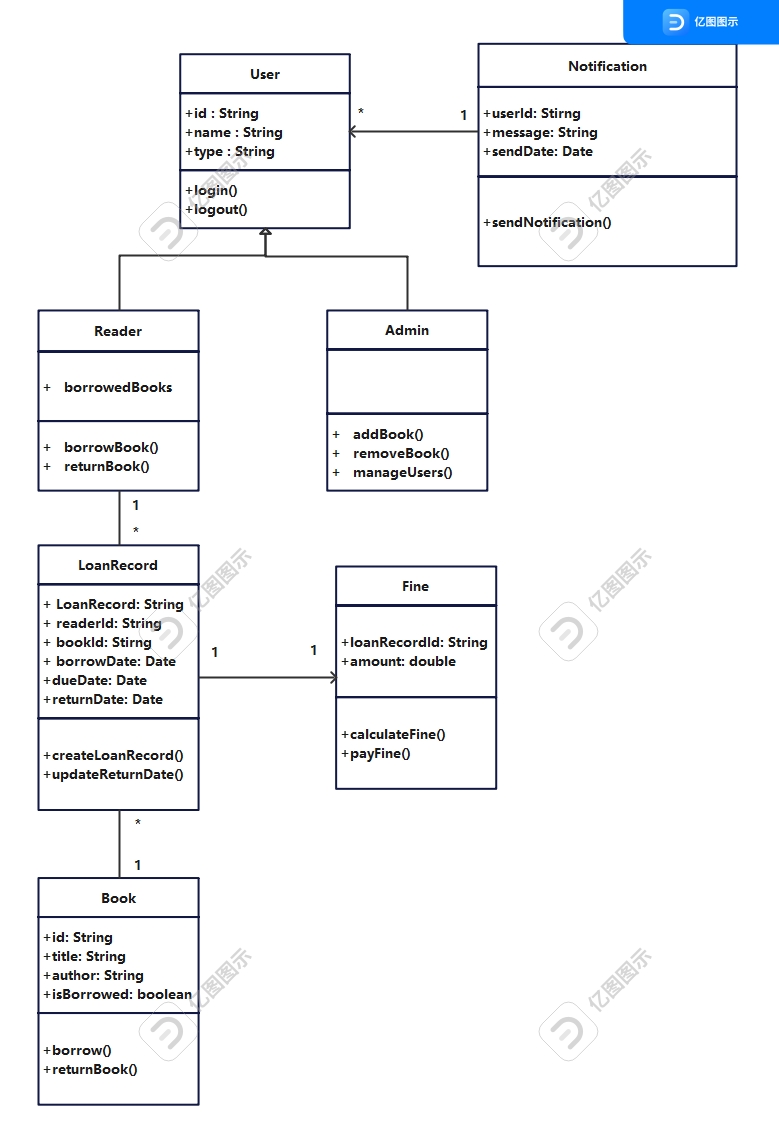
- 因为用户是读者和管理员的父类,所以读者和管理员继承用户类。
- 一个借阅记录关联一个读者,一个读者可以有多个借阅记录,因此借阅记录与读者是双向关联。
- 当查询一本书的借阅历史时,可以查看到借阅记录;查看一位读者的借阅历史时,也可以查看到借了哪些书籍,因此借阅记录与书籍是双向关联。
- 借阅记录可以触发罚款,但罚款不一定总是由借阅记录触发,也有可能是损坏图书,因此借阅记录与罚款是单向关联。
- 通知信息可以向任何用户发送,他们之间属于一对多的关系。
tips: 单向关联: 在这个场景中,借阅记录是导致罚款的一个可能原因,但罚款本身并不直接影响借阅记录。也就是说,借阅记录的存在可以触发罚款,但罚款的发生不会改变原有的借阅记录。 双向关联: 如果两者之间存在相互影响,即一个的变化会导致另一个也发生变化,那么这就是双向关联。但在本例中,罚款的发生并不会改变借阅记录的内容。
对象图
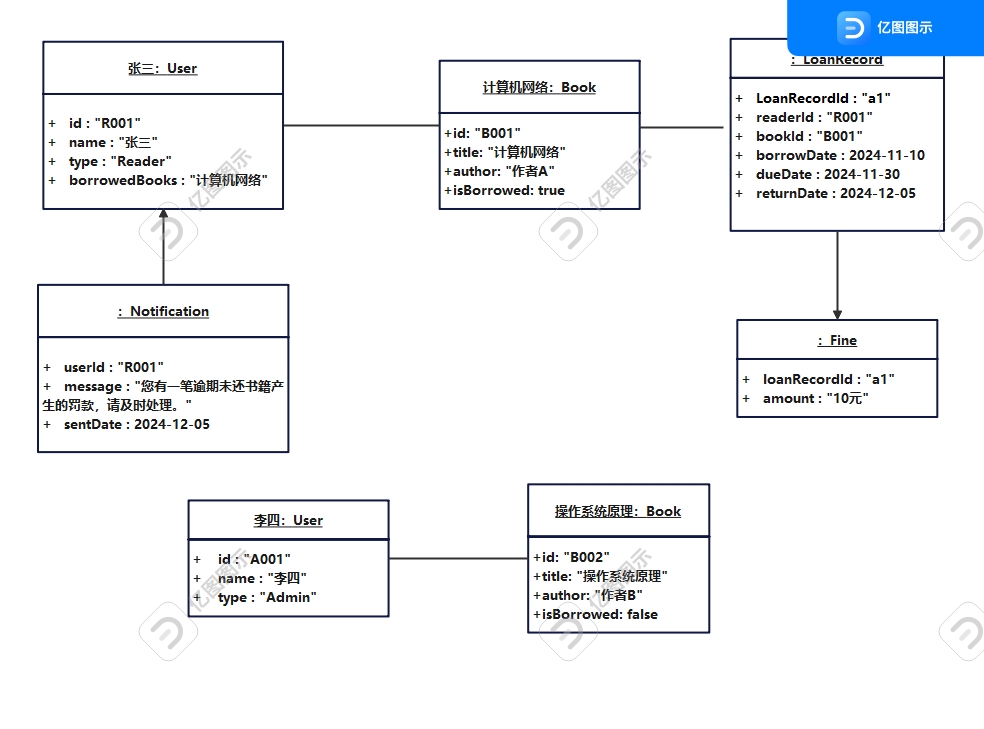
- 借阅过程 张三 → 借阅《计算机网络》 → 借阅记录
- 罚款生成 借阅记录(实际归还日期晚于应归还日期) → 罚款金额
- 通知发送 系统 → 创建罚款通知 → 发送至张三
- 管理员操作 管理员 → 添加《操作系统原理》
tips 对象图中的链接方向通常与类图中的关联方向相对应。在类图中,如果关联被标记为单向(通常通过带有箭头的实线表示),则对象图中的链接也将是单向的。如果类图中的关联是双向的(通常通过不带箭头的实线或两端都有箭头的实线表示),则对象图中的链接也将是双向的。
根据类图转换代码
User
public class User {
String id;
String name;
String type;
public User(String id,String name,String type) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
}
public void login() {
System.out.println(name + "logged in");
}
public void logout() {
System.out.println(name + "logged out");
}
}
Book
public class Book {
String id;
String title;
String author;
boolean isBorrowed;
public Book(String id, String title, String author) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
this.isBorrowed = false;
}
public void borrow() { //借出
this.isBorrowed = true;
}
public void returnBook() { //归还
this.isBorrowed = false;
}
}
Reader
class Reader extends User{
private List<Book> borrowedBooks;
public Reader(String id, String name) {
super(id, name, "读者");
this.borrowedBooks = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void borrowBook(Book book) { //借书
book.borrow();
borrowedBooks.add(book);
System.out.println("成功借阅书籍: " + book.title);
}
public void returnBook(Book book) { //还书
book.returnBook();
borrowedBooks.remove(book);
System.out.println("成功归还书籍: " + book.title);
}
}
Admin
class Admin extends User {
private List<User> users;
public Admin(String id, String name) {
super(id, name, "管理员");
this.users = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addBook(Book book) {
System.out.println("添加书籍:" + book.title);
}
public void removeBook(Book book) {
System.out.println("移除书籍: " + book.title);
}
public void addUser(User user) {
users.add(user);
System.out.println(" added user: " + user.name);
}
public void removeUser(String userId) {
User userToRemove = null;
for (User user : users) {
if (user.id.equals(userId)) {
userToRemove = user;
break;
}
}
if (userToRemove != null) {
users.remove(userToRemove);
System.out.println(" removed user: " + userToRemove.name);
} else {
System.out.println("User with ID " + userId + " not found.");
}
}
public void manageUsers() {
System.out.println("Managing users...");
Reader newReader = new Reader("R002", "李五");
addUser(newReader);
removeUser("R001");
}
}
LoanRecord
class LoanRecord {
String loanRecordId;
String readerId;
String bookId;
Date borrowDate;
Date dueDate;
Date returnDate;
public LoanRecord(String loanRecordId, String readerId, String bookId, Date borrowDate, Date dueDate) {
this.loanRecordId = loanRecordId;
this.readerId = readerId;
this.bookId = bookId;
this.borrowDate = borrowDate;
this.dueDate = dueDate;
}
public void createLoanRecord() {
System.out.println("创建借阅记录: " + bookId);
}
public void updateReturnDate(Date returnDate) {
this.returnDate = returnDate;
}
}
Fine
class Fine {
String loanRecordId;
double amount;
public Fine(String loanRecordId, double amount) {
this.loanRecordId = loanRecordId;
this.amount = amount;
}
public double calculateFine() {
return (amount > 0) ? amount : 0; // 超期天数大于0才计算罚款
}
public void payFine() {
System.out.println("Fine of " + amount + " paid.");
}
}
Notification
class Notification {
String userId;
String message;
Date sentDate;
public Notification(String userId, String message, Date sentDate) {
this.userId = userId;
this.message = message;
this.sentDate = sentDate;
}
public void sendNotification() {
System.out.println("Notification to " + userId + ": " + message);
}
}
本文章使用limfx的vscode插件快速发布