参数配置框架搭建
简述
在我们设计的采集系统上加了参数配置模块的原型,目前设计时这样的:
参数配置采用读取一个名为config.yml的文件,然后再通过驱动,系统调用,axi_lite传到PL端,这样之后外界想要配置参数的话,就想办法修改这个yaml文件就可以了
然后参数配置和运行采集并进行DMA传输分别是两个可执行程序:para_app和nvme_dma,对于外界来说,就是先将配置写入yaml文件,然后执行一下para_app,就相当于确认配置修改了,再运行以下nvme_app,就相当于开始采集并DMA传输了
这里参数配置功能仅仅搭了个原型,需要配置什么参数还需要添加
详细设计
PL部分
目前传到PL端的参数还未投入使用,仅仅是传到了PL端,因为我这里还没加上龙哥的程序(verilog-ethernet部分),而这些参数都是用来配置那verilog-ethernet的
问题:之前我尝试用龙哥的程序进行测试,就采集波形然后在PL端显示,但结果不太理想
我之前是将龙哥程序整个塞进我的程序里,目前我在考虑要不要将龙哥程序细分拆解到我的block design内
这样就可以先不管输入部分,可以直接将参数配置和verilog-ethernet进行配合
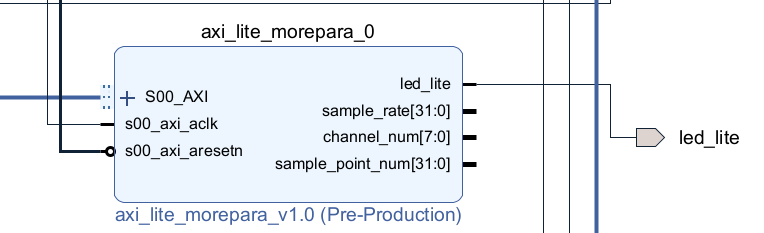
PS部分
关于参数配置有三个相关文件,分别为保存配置信息的config.yml文件,参数配置驱动文件para_drv.c,参数配置应用文件para_app.c
首先是config.yml的内容,非常简单,这里有一些是pl_led,输入1会让对应的led亮,0会让对应的led灭,主要用来标志参数是否传到的PL端
zynqmp:
pl_led: 1
sample_rate: 2000000
channel_num: 8
sample_point_num: 1000000
然后是para_drv.c的内容,这个驱动文件规定了参数是如何通过寄存器传到PL端的
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/of_platform.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
struct AxiUserGpio
{
int addr_width;
int data_width;
struct device_node *dev_node;
int reg_num;
unsigned int *reg_value;
};
struct AxiUserGpio *AxiUserGpio_data;
static int key_major;
static struct class *key_cls;
static unsigned int *AxiData_0 = NULL;
static unsigned int *AxiData_1 = NULL;
static unsigned int *AxiData_2 = NULL;
static unsigned int *AxiData_3 = NULL;
//注意这里.compatible的字符串和pl.dtsi中的属性是相对应的
static struct of_device_id AxiUserGpio_of_match[] = {
{.compatible = "xlnx,axi-lite-morepara-1.0"},
{},
};
int of_AxiUserGpio_data(struct AxiUserGpio *pdata, struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct device_node *np = pdev->dev.of_node;
int ret = 0;
pdata->reg_num = of_property_count_elems_of_size(np, "reg", sizeof(int));
if (pdata->reg_num < 0)
{
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "get reg_num failed\n");
return ret;
}
pdata->reg_value = (unsigned int *)kmalloc(sizeof(unsigned int) * pdata->reg_num, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pdata->reg_value)
{
kfree(pdata->reg_value);
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "kmalloc failed\n");
return -1;
}
ret = of_property_read_u32_array(np, "reg", pdata->reg_value, pdata->reg_num);
if (ret != 0)
{
kfree(pdata->reg_value);
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "get reg failed\n");
return ret;
}
ret = of_property_read_u32(np, "xlnx,s00-axi-addr-width", &pdata->addr_width);
if (ret < 0)
{
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "get addr_width failed\n");
return ret;
}
ret = of_property_read_u32(np, "xlnx,s00-axi-data-width", &pdata->data_width);
if (ret < 0)
{
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "get data_width failed\n");
return ret;
}
return 0;
}
static int AxiUserGpio_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int ret = 0;
int i = 0;
struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;
struct AxiUserGpio *pdata = dev_get_platdata(dev);
if (!pdata)
{
pdata = devm_kzalloc(dev, sizeof(struct AxiUserGpio), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pdata)
return -ENOMEM;
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, pdata);
}
ret = of_AxiUserGpio_data(pdata, pdev);
AxiUserGpio_data = pdata;
// 打印属性值
printk("addr_width = %d\r\n", AxiUserGpio_data->addr_width);
printk("data_width = %d\r\n", AxiUserGpio_data->data_width);
printk("reg_num = %d\r\n", AxiUserGpio_data->reg_num);
for (i = 0; i < AxiUserGpio_data->reg_num; i += 2)
{
printk("reg = %#X %#X \r\n", AxiUserGpio_data->reg_value[i], AxiUserGpio_data->reg_value[i + 1]);
}
AxiData_0 = ioremap(AxiUserGpio_data->reg_value[1] + 4 * 0, 4);
AxiData_1 = ioremap(AxiUserGpio_data->reg_value[1] + 4 * 1, 4);
AxiData_2 = ioremap(AxiUserGpio_data->reg_value[1] + 4 * 2, 4);
AxiData_3 = ioremap(AxiUserGpio_data->reg_value[1] + 4 * 3, 4);
return ret;
}
static int AxiUserGpio_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
kfree(AxiUserGpio_data->reg_value);
iounmap(AxiData_0);
iounmap(AxiData_1);
iounmap(AxiData_2);
iounmap(AxiData_3);
return 0;
}
int AxiUserGpio_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
printk("axi gpio open\n");
return 0;
}
ssize_t AxiUserGpio_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *fops) //用户发送,内核读取信息并打印
{
printk("count = %d\r\n", count);
int flag = 0;
int a[4]={0};
flag = copy_from_user(a, buf, count); //使用copy_from_user读取用户态发送过来的数据
int pl_led=a[0];
int sample_rate=a[1];
int channel_num=a[2];
int sample_point_num=a[3];
if (flag == 0)
{
printk(KERN_CRIT "Kernel receive data: %d\n", pl_led);
}
else
{
printk("Kernel receive data failed!\n");
}
writel(pl_led, AxiData_0);
writel(sample_rate, AxiData_1);
writel(channel_num, AxiData_2);
writel(sample_point_num, AxiData_3);
printk("-para write-\n");
return 0;
}
int AxiUserGpio_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
printk("axi gpio close\n");
return 0;
}
const struct file_operations key_fops = {
.open = AxiUserGpio_open,
.write = AxiUserGpio_write,
.release = AxiUserGpio_close,
};
static struct platform_driver AxiUserGpio_device_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "AxiUserGpio",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(AxiUserGpio_of_match),
},
.probe = AxiUserGpio_probe,
.remove = AxiUserGpio_remove,
};
static int __init AxiUserGpio_init(void)
{
key_major = register_chrdev(0, "axi_gpio_para", &key_fops);
if (key_major < 0)
{
printk("register chrdev faile!\n");
return key_major;
}
printk("register chrdev ok!\n");
key_cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "key_class");
printk("class create ok!\n");
device_create(key_cls, NULL, MKDEV(key_major, 0), NULL, "gpio_para%d", 0);
printk("device create ok!\n");
return platform_driver_register(&AxiUserGpio_device_driver);
}
static void __exit AxiUserGpio_exit(void)
{
device_destroy(key_cls, MKDEV(key_major, 0));
//删除类
class_destroy(key_cls);
//注销主设备号
unregister_chrdev(key_major, "axi_gpio_para");
platform_driver_unregister(&AxiUserGpio_device_driver);
}
late_initcall(AxiUserGpio_init);
module_exit(AxiUserGpio_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("uisrc");
最后是para_app.c的内容,功能是读取config.yml,然后将内容传到驱动文件中
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
typedef struct {
int pl_led;
int sample_rate;
int channel_num;
int sample_point_num;
} Config;
int parse_yaml(const char *filename, Config *config) {
FILE *file = fopen(filename, "r");
if (!file) {
perror("Failed to open file");
return -1;
}
char line[256];
while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), file)) {
// Remove trailing newline
line[strcspn(line, "\n")] = 0;
if (strstr(line, "pl_led")) {
sscanf(line, " pl_led: %d", &config->pl_led);
} else if (strstr(line, "sample_rate")) {
sscanf(line, " sample_rate: %d", &config->sample_rate);
} else if (strstr(line, "channel_num")) {
sscanf(line, " channel_num: %d", &config->channel_num);
} else if (strstr(line, "sample_point_num")) {
sscanf(line, " sample_point_num: %d", &config->sample_point_num);
}
}
fclose(file);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Config config = {0};
const char *filename = "/home/uisrc/config.yml";
if (parse_yaml(filename, &config) == 0) {
printf("pl_led: %d\n", config.pl_led);
printf("sample_rate: %d\n", config.sample_rate);
printf("channel_num: %d\n", config.channel_num);
printf("sample_point_num: %d\n", config.sample_point_num);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error parsing YAML file.\n");
return 1;
}
int fd = 0;
int retvalue = 0;
int a[4]={0};
fd = open("/dev/gpio_para0", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open fail!\n");
exit(1);
}
a[0]=config.pl_led;
a[1]=config.sample_rate;
a[2]=config.channel_num;
a[3]=config.sample_point_num;
retvalue = write(fd, a, sizeof(a)); //写数据
if (retvalue < 0)
{
printf("Write led failed!\n");
}
else
{
printf("Write led success!\n");
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
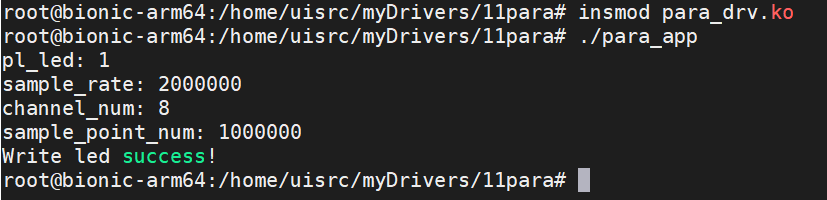
运行结果
本文章使用limfx的vscode插件快速发布