计组实验-MIPS
Mars
官网:MARS MIPS simulator - Missouri State University
一方面按照实验指导书的入门教程,另有官网的Tutorials
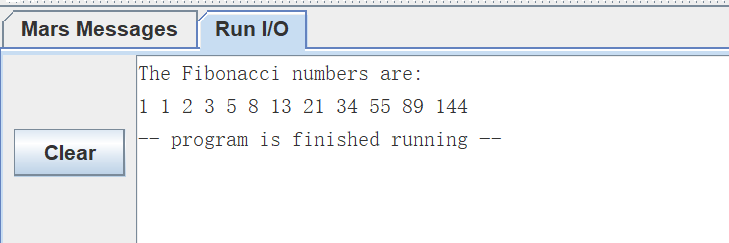
首先可以运行一下示例代码:fibonacci
# Compute first twelve Fibonacci numbers and put in array, then print
.data
fibs: .word 0 : 12 # "array" of 12 words to contain fib values
size: .word 12 # size of "array"
.text
la $t0, fibs # load address of array
la $t5, size # load address of size variable
lw $t5, 0($t5) # load array size
li $t2, 1 # 1 is first and second Fib. number
add.d $f0, $f2, $f4
sw $t2, 0($t0) # F[0] = 1
sw $t2, 4($t0) # F[1] = F[0] = 1
addi $t1, $t5, -2 # Counter for loop, will execute (size-2) times
loop: lw $t3, 0($t0) # Get value from array F[n]
lw $t4, 4($t0) # Get value from array F[n+1]
add $t2, $t3, $t4 # $t2 = F[n] + F[n+1]
sw $t2, 8($t0) # Store F[n+2] = F[n] + F[n+1] in array
addi $t0, $t0, 4 # increment address of Fib. number source
addi $t1, $t1, -1 # decrement loop counter
bgtz $t1, loop # repeat if not finished yet.
la $a0, fibs # first argument for print (array)
add $a1, $zero, $t5 # second argument for print (size)
jal print # call print routine.
li $v0, 10 # system call for exit
syscall # we are out of here.
######### routine to print the numbers on one line.
.data
space:.asciiz " " # space to insert between numbers
head: .asciiz "The Fibonacci numbers are:\n"
.text
print:add $t0, $zero, $a0 # starting address of array
add $t1, $zero, $a1 # initialize loop counter to array size
la $a0, head # load address of print heading
li $v0, 4 # specify Print String service
syscall # print heading
out: lw $a0, 0($t0) # load fibonacci number for syscall
li $v0, 1 # specify Print Integer service
syscall # print fibonacci number
la $a0, space # load address of spacer for syscall
li $v0, 4 # specify Print String service
syscall # output string
addi $t0, $t0, 4 # increment address
addi $t1, $t1, -1 # decrement loop counter
bgtz $t1, out # repeat if not finished
jr $ra # return之后敲一些简 单的指令入门,通过单步调试可以看出寄存器的变化
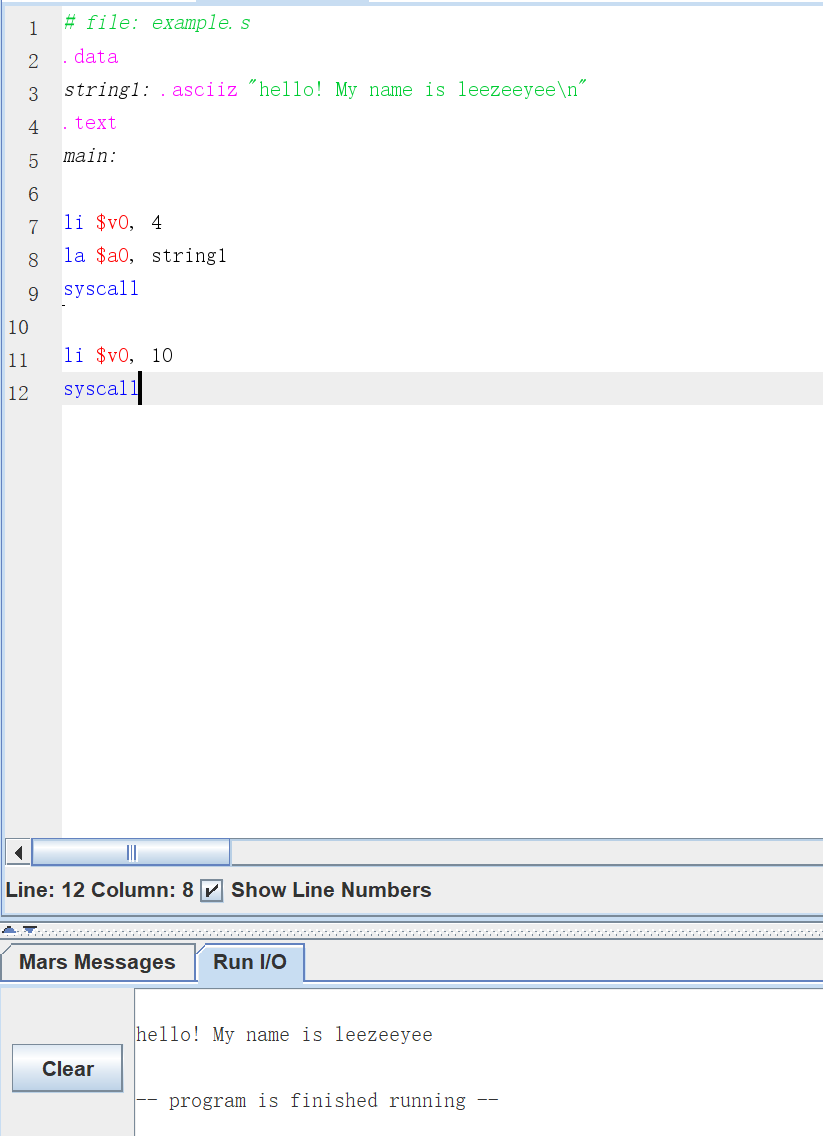
hello world
保存
算术运算实验
问题
变量A-F可以存储在暂存寄存器中,最终结果Z必须存储在内存变量并输出。建议用十进制显示数据段寄存器的值,以方便观察结果。
//Arithmetic.c
#include<stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int A= 15;
int B=10;
int C=7;
int D=2;
int E=18;
int F=-3;
int Z=0;
Z= (A+B)+ (C-D)+ (E+F)- (A-C) ;
printf ("%x",Z) ;
return 0;
}
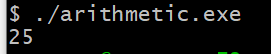
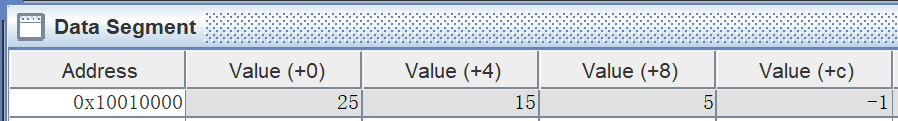
编译后打印结果在16进制表示为0x25
汇编代码
# file: arithmetic.asm
# author: leezeeyee
# date: 2020/12/6
.data
result: .word 1
.text
main:
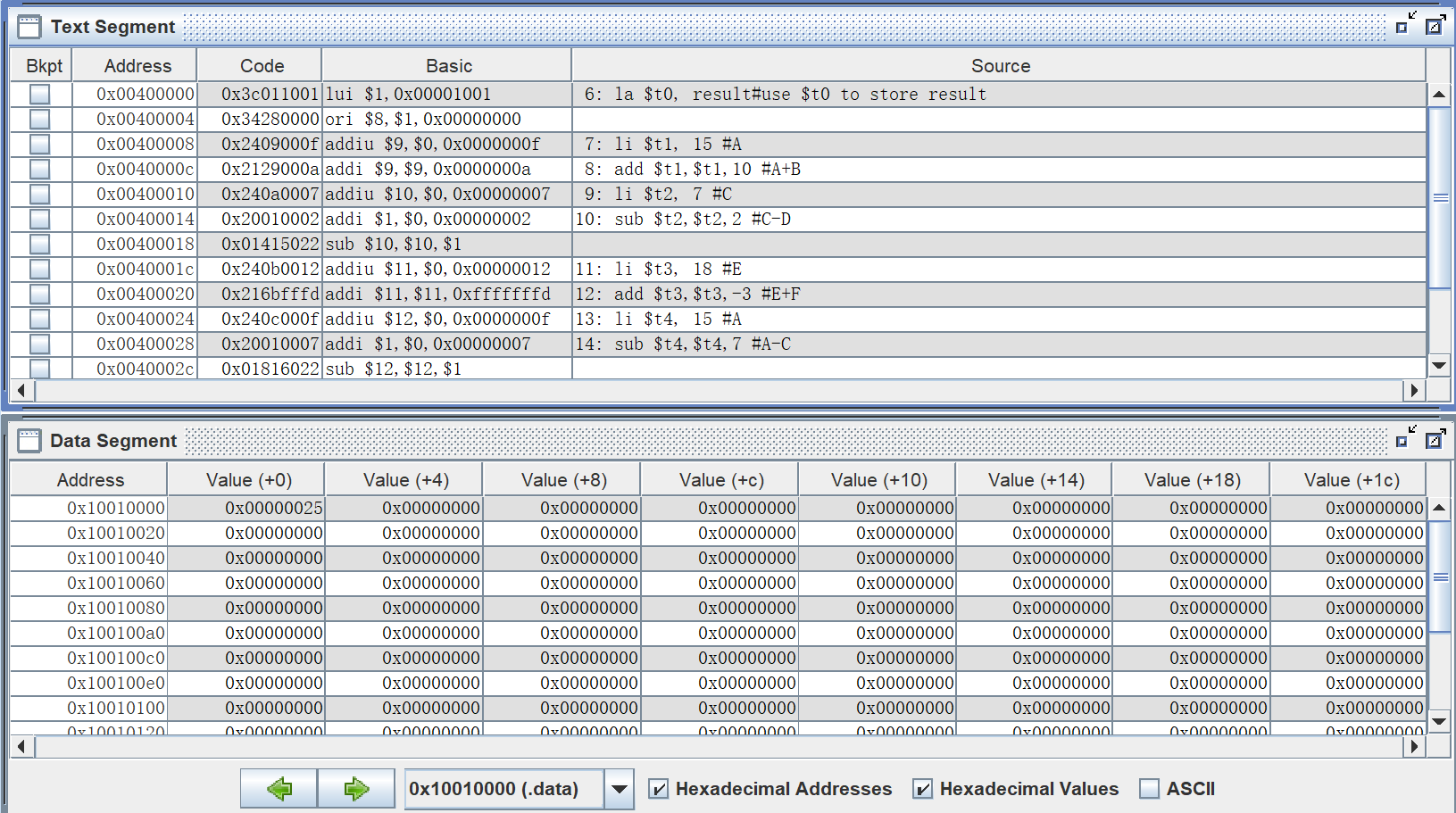
la $t0, result#use $t0 to store result
li $t1, 15 #A
add $t1,$t1,10 #A+B
li $t2, 7 #C
sub $t2,$t2,2 #C-D
li $t3, 18 #E
add $t3,$t3,-3 #E+F
li $t4, 15 #A
sub $t4,$t4,7 #A-C
add $t1,$t1,$t2 #(A+B)+ (C-D)
sub $t3,$t3,$t4# (E+F)- (A-C)
add $t1,$t1,$t3 #(A+B)+ (C-D)+(E+F)- (A-C)
sw $t1, ($t0)# save result
结果
可见,最后保存到内存中的结果也为0x25
分支结构实验
编写一段MIPS汇编程序,完成与如下C语言代码完全相同的功能。变量A~C、Z必须是内存中的整型变量,程序运行过程中可以加载到寄存器,每次运行之前可以修改A~C的初始值。注意,可以使用MIPS中与分支相关的伪指令,使得比较和分支代码更为简单,建议用十进制显示数据段的值,以方便观察结果。
//Branch.c
int main()
{
//Note: I should be able to change the values of A, B, and C when testing
//your code, and get correct output each time!(i.e.don't just hardwire your output)
int A = 10; int B = 15; int C = 6; int Z = 0;
if (A > B || C < 5)
Z = 1;
else if (A == B)
Z = 2;
else
Z = 3;
switch (Z)
{
case 1:
Z = -1;
break;
case 2:
Z = -2;
break;
default:
Z = 0;
break;
}
}保证内存中的为整型变量
分支跳转通过jump的延伸实现
汇编代码
update:use lw $t5,A to replace
la $t1,A# load address of A into $t1
lw $t5,($t1)# load data A from address in $t1# file: branch.asm
# author: leezeeyee
# date: 2020/12/6
.data
A: .word 25
B: .word 15
C: .word 5
Z: .word 0
.text
main:
lw $t5,A# load data A in $t5
lw $t6,B# load data B in $t6
lw $t7,C# load data C in $t7
lw $t8,Z# load data Z in $t8
bgt $t5,$t6,L10#A>B
blt $t7,5,L10#C<5
j L110
L10:
li $t8,1#Z=1
j L20
L110:
beq $t5,$t6,L11#A==B
li $t8,3#Z=3#else
j L20
L11:
li $t8,2#Z=2
L20:
beq $t8,1,L3#z==1
j L4
L3:
li $t8,-1#Z=-1
j L7#break
L4:
beq $t8,2,L5#z==2
j L6#default
L5:
li $t8,-2#Z=-2
j L7#break
L6:
li $t8,0#Z=0
L7:
sw $t8,Z# file: branch.asm
# author: leezeeyee
# date: 2020/12/6
.data
A: .word 25
B: .word 15
C: .word 5
Z: .word 0
.text
main:
la $t1,A# load address of A into $t1
la $t2,B# load address of B into $t2
la $t3,C# load address of C into $t3
la $t4,Z# load address of Z into $t4
lw $t5,($t1)# load data A from address in $t1
lw $t6,($t2)# load data B from address in $t2
lw $t7,($t3)# load data C from address in $t3
lw $t8,($t4)# load data Z from address in $t4
bgt $t5,$t6,L10#A>B
blt $t7,5,L10#C<5
j L110
L10:
li $t8,1#Z=1
j L20
L110:
beq $t5,$t6,L11#A==B
li $t8,3#Z=3#else
j L20
L11:
li $t8,2#Z=2
L20:
beq $t8,1,L3#z==1
j L4
L3:
li $t8,-1#Z=-1
j L7#break
L4:
beq $t8,2,L5#z==2
j L6#default
L5:
li $t8,-2#Z=-2
j L7#break
L6:
li $t8,0#Z=0
L7:
sw $t8,($t4)结果展示
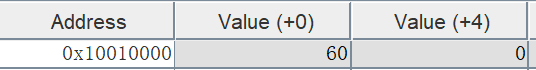
C<5,Z=-1
A==B,Z=-2
A>B,Z=-1
循环结构实验
编写一段MIPS汇编程序, 完成与如下C语言代码完全相同的功能。变量i和Z必须是内存中的整型变量, 程序运行过程中可以加载到寄存器,每次运行之前可以修改i.Z的初始值。注意, 可以使用MIPS中与分支相关的伪指令, 使得比较和分支代码更为简单, 建议用十进制显示数据段的值, 以方便观察结果。
//Loop.c
int main() {
int Z = 2;
int i = 40;
do {
Z++;
} while (Z < 100);
while (i > 0) {
Z--;
i--;
}
}汇编代码
# file: loop.asm
# author: leezeeyee
# date: 2020/12/6
.data
Z: .word 2
i: .word 40
.text
main:
lw $t1,Z
lw $t2,i
Loop1:
add $t1,$t1,1
blt $t1,100,Loop1
bgt $t2,0,Loop2
Loop2:
sub $t1,$t1,1
sub $t2,$t2,1
bgt $t2,0,Loop2
#store result
sw $t1,Z
sw $t2,i结果展示
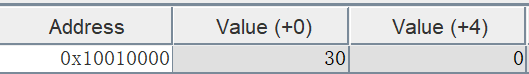
z=2,i=40
z=2,i=70
数据访问实验
编写一段MIPS汇编程序, 完成与如下C语言代码完全相同的功能。变量A和B必须是内存中的整型数组, C是内存整型变量, i可以是寄存器, 建议用十进制显示数据段的值,以方便观察结果。
//array.c
int main()
{
int A[5];
//Empty memory region for 5 elements
int B[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int C = 10;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
A[i] = B[i] + C;
}
}小结
可以通过两种方法进行地址偏移,一种是直接通过指令提供的格式,形如:
sw $t1,4($t0)第二种便是先计算出偏移后的地址,再访问,即:
add $t0,$t0,4
sw $t1,($t0)这种方法的好处在于可以对偏移量进行控制,在循环中可以得到应用
汇编代码
# file: array.asm
# author: leezeeyee
# date: 2020/12/6
.data
A: .space 20#5*4(int)
B: .space 20#5*4(int)
C: .word 10
.text
main:
#initial array B using loop
la $t0,B
li $t1,0
blt $t1,5,iniB
iniB:
#add $t2,$t#inital value B=i
add $t1,$t1,1
sw $t1,($t0)
add $t0,$t0,4
blt $t1,5,iniB
#update array A using loop
la $t0,A
li $t1,0
la $t3,B
lw $t5,C
blt $t1,5,updateA
updateA:
lw $t4,($t3) # $t4=B[i]
add $t6,$t4,$t5 # $t6=B[i]+C
#li $t2,0#inital value A=0
sw $t6,($t0) # A[i]=$t6
add $t0,$t0,4
add $t1,$t1,1
add $t3,$t3,4
blt $t1,5,updateA
结果展示
初始化数据
最终结果
数据排序实验
编写一段MIPS汇编程序,完成与如下C语言代码完全相同的功能。变量A必须是内存中的整型数组,必须使用MIPS过程调用机制实现对应C语言函数,建议用十进制显示数据段和寄存器的值,以方便观察结果。
//array_ sort.c
//交换函数,如果x指针指向的内存变量>y指针指向的内存变量,交换内存变量,返回1,否则返回0
int swap(int* x, int* y)
{
if (*x > * y)
{
int t = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = t;
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int A[16] = { 10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0,-1,-2,-3,-4,-5 };
int i, j, counter = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 15; i++)
//冒泡排序算法
for (j = i + 1; j < 16; j++)
counter += swap(&A[i], &A[j]); //counter 统计交换次数
printf("%d", counter);
}汇编代码
# file: array_sort.asm
# author: leezeeyee
# date: 2020/12/6
.data
A: .space 68#16*4(int)
counter: .word 0
testX: .word 7
testY: .word 5
.text
#initial array A
la $t0,A
li $t1,0
li $t5,10
blt $t1,16,iniA
iniA:
sub $t2,$t5,$t1#inital value A=10-i
sw $t2,($t0)
add $t0,$t0,4
add $t1,$t1,1
blt $t1,16,iniA
#loop
la $t5,A
li $t6,0#i=0
lw $s0,counter
#li $t7,0#counter=0
fori:
add $t7,$t6,1#j=i+1
forj:
sll $t8,$t6,2#i*4
sll $t9,$t7,2#j*4
add $t0,$t5,$t8#A[i]
add $t1,$t5,$t9#A[j]
jal swap
return:
add $s0,$s0,$v0
add $t7,$t7,1
blt $t7,16,forj#end of forj
add $t6,$t6,1
blt $t6,15,fori#end of fori
j end
#input address $t0,$t1
swap:#to swap value in address if x>y
lw $t2,($t0)
lw $t3,($t1)
bgt $t2,$t3,L
li $v0,0
j next
L:
sw $t3,($t0)
sw $t2,($t1)
li $v0,1
#return value in $v0
next:
jr $ra
end:
#save counter
sw $s0,counter思路
首先写出子函数,swap
# file: array_sort.asm
# author: leezeeyee
# date: 2020/12/6
.data
A: .space 64#16*4(int)
testX: .word 3
testY: .word 5
.text
la $t0,testX
la $t1,testY
#input address $t0,$t1
swap:#to swap value in address if x>y
lw $t2,($t0)
lw $t3,($t1)
bgt $t2,$t3,L
li $v0,0
j next
L:
sw $t3,($t0)
sw $t2,($t1)
li $v0,1
#return value in $v0
next:
nop结果展示
初始化数组A
swap:
x<y,不变,返回值为0
x>y,交换,返回值为1
排序结果:
错误
Error in : invalid program counter value: 0x00000000
是因为数组出界